
Sustainable Food Packaging Solutions for a Greener Future
Share
The New Economics of Sustainable Food Packaging
The demand for sustainable food packaging is no longer a niche market trend; it's a core business requirement. Driven by a combination of changing consumer preferences, stricter regulations, and corporate commitments to social responsibility, businesses are realizing that eco-friendly packaging makes economic sense and offers a competitive edge. This shift provides a significant opportunity for companies to reduce their environmental impact while also boosting their brand image and profitability.
Key Drivers of Change
Several interconnected forces are driving the move towards sustainable food packaging:
-
Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental consequences of their buying habits. They actively look for products with eco-friendly packaging, rewarding businesses that make sustainability a priority.
-
Regulatory Pressure: Governments around the world are enacting tougher rules to combat plastic pollution and promote sustainable packaging. This evolving regulatory landscape presents both obstacles and openings for businesses to navigate.
-
Corporate Sustainability Goals: Many organizations are establishing ambitious sustainability targets, including minimizing packaging waste and shifting to renewable resources. These targets are driving innovation and investment in sustainable packaging technologies.
-
Brand Differentiation: In a competitive market, sustainable packaging can set a brand apart. It allows companies to resonate with environmentally conscious consumers and cultivate a positive brand image.
The infographic below illustrates the current breakdown of food packaging types, highlighting the prevalence of plastic and the rise of compostable and recyclable options.
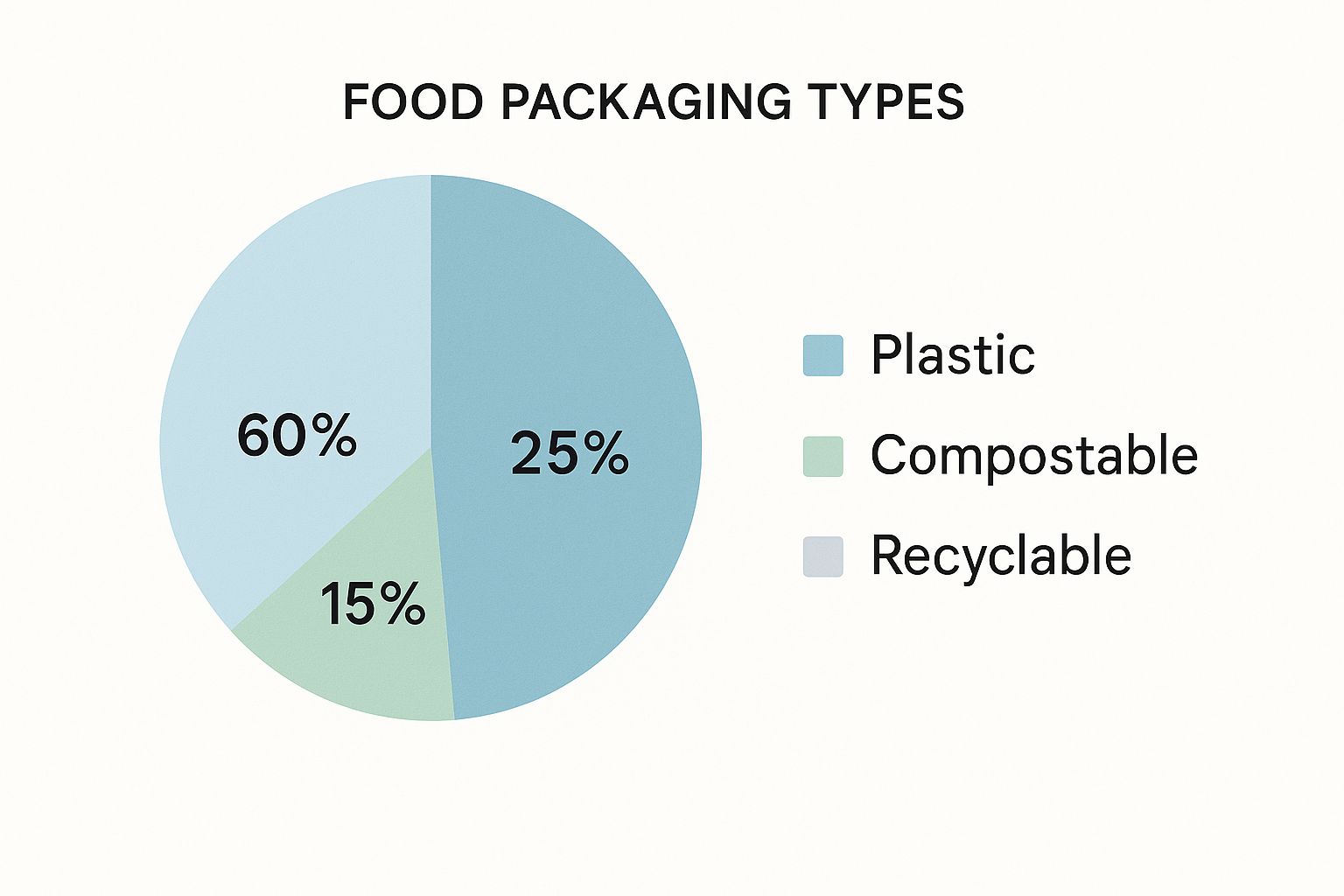
As shown, plastic still accounts for a significant 60% of food packaging. However, the growing market share of compostable (25%) and recyclable (15%) materials points to a definitive trend toward sustainability. This shift underlines the ongoing transformation within the packaging industry.
A Growing Global Market
The global sustainable packaging market is experiencing substantial growth. Market projections predict a significant rise from approximately $292.71 billion in 2024 to $423.56 billion by 2029, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 7%. Find more detailed statistics here. Europe currently dominates the market, with over 30% global market share, driven by strong regulations and high consumer awareness. The Asia Pacific region, meanwhile, is expected to experience the fastest growth, with a projected CAGR exceeding 7% through 2030, propelled by a growing middle class and increasingly strict environmental regulations.
To provide a clearer view of regional growth, the following table shows market share and projected growth across key geographic areas.
Global Sustainable Packaging Market Growth by Region
| Region | Current Market Share | Projected CAGR | Key Growth Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | 30%+ | ~7% | Stringent Regulations, Consumer Awareness |
| Asia Pacific | - | 7%+ | Growing Middle Class, Environmental Policies |
| North America | - | - | Increasing Corporate Sustainability Initiatives |
| Rest of World | - | - | Emerging Markets, Focus on Waste Reduction |
This table highlights the regional variations in market share and growth drivers. Europe's strong regulatory environment and consumer focus on sustainability contribute to its leading position. The Asia Pacific region's rapid growth is fueled by a burgeoning middle class and increased environmental consciousness.
From Cost Center to Competitive Edge
Sustainable packaging has traditionally been viewed as a cost center. However, this perception is changing. As the market matures and technology evolves, sustainable options are becoming more and more cost-competitive. Additionally, the benefits extend well beyond just cost savings. Companies adopting sustainable packaging can:
-
Attract and Retain Customers: Consumers are increasingly willing to pay more for sustainably packaged products, resulting in higher sales and greater customer loyalty.
-
Enhance Brand Reputation: Showing a commitment to sustainability builds consumer trust and reinforces a positive brand image.
-
Reduce Operational Costs: Optimizing package design and using eco-friendly materials can reduce material consumption, lower transportation expenses, and decrease waste disposal fees.
-
Gain a Competitive Advantage: By staying ahead of regulations and anticipating consumer demands, companies can differentiate themselves from competitors and secure a larger market share.
This evolving economic landscape presents a compelling argument for businesses to prioritize sustainable food packaging. By understanding the long-term value and competitive advantages of environmentally sound practices, businesses can ensure their future success in a rapidly evolving market.
Why Consumers Are Driving the Packaging Revolution
Consumer behavior is dramatically changing the food industry, with sustainable food packaging leading the charge. Consumers now demand transparency and accountability from sourcing to disposal – it's no longer enough for a product just to taste good. This shift signifies a fundamental change in purchasing decisions.

The Psychology of Sustainable Choices
Traditionally, price, taste, and convenience drove consumer choices. Now, environmental and social responsibility play an increasing role. This growing awareness translates to supporting businesses aligned with consumer values. For instance, a consumer might choose compostable packaging over conventional plastic, even at a higher price, recognizing the long-term costs of unsustainable practices.
The Power of Consumer Preference
Consumer preferences are reshaping the sustainable food packaging sector. A 2025 consumer report revealed that 54% of respondents intentionally chose sustainably packaged products in the past six months. This demonstrates a shift towards prioritizing eco-friendly packaging alongside quality and price. Explore this topic further. This demand pushes brands to invest in eco-friendly solutions.
Building Brand Loyalty Through Sustainability
Younger demographics and urban populations are more inclined to pay more for sustainably packaged goods. Brands targeting these demographics must prioritize sustainable packaging to stay competitive. Brands adopting sustainable solutions report increased customer loyalty and better market positioning, encouraging the shift from traditional plastics to recyclable, compostable, or bio-based alternatives.
Communicating Sustainability Effectively
Switching materials isn't enough; brands must effectively communicate their sustainability initiatives. This involves:
- Transparent Labeling: Clearly indicating environmental benefits (e.g., "recyclable," "compostable").
- Educational Campaigns: Raising awareness about sustainable packaging's environmental impact.
- Storytelling: Sharing the brand's sustainability journey and efforts to reduce environmental impact.
- Engaging Content: Creating content that resonates with consumers and promotes sustainable choices.
By communicating their commitment to sustainability, brands build trust, strengthen their image, and boost sales. Embracing sustainable packaging benefits both the environment and profits. It's an investment in the future of the food industry and the planet.
Material Innovations Reshaping Food Packaging
Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable practices from the food industry, pushing companies to rethink their packaging. This exploration delves into the innovative materials revolutionizing the sector, highlighting the advantages and challenges of each. From familiar paper-based solutions to the rise of bioplastics, and even exploring the potential of mushrooms and seaweed, understanding these materials is crucial for businesses embracing a greener future.
Reinventing Paper and Paperboard
Paper and paperboard, already widely recycled and accepted by consumers, hold a significant portion of the sustainable packaging market. Innovations are focused on improving their functionality and expanding their applications. Bio-based coatings, for example, are enhancing paper's resistance to grease and moisture, enabling its use with a greater variety of food products. This allows companies to retain the familiar benefits of paper while overcoming its traditional limitations.
Advancements in paper recycling technologies are further minimizing environmental impact by improving the quality of recycled paper. This creates a closed-loop system, reducing the need for virgin materials and minimizing waste. These developments are crucial for reducing the environmental footprint of paper packaging.
The Rise of Bioplastics
Bioplastics, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, present a compelling alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. These materials can biodegrade under specific conditions, diverting waste from landfills and lessening plastic pollution. However, scalability and cost remain significant hurdles to wider bioplastic adoption. Ensuring compatibility with existing recycling infrastructure is also essential for maximizing their environmental benefits. This is vital to avoid contamination of traditional recycling streams and ensure efficient processing.
Exploring Mushroom and Seaweed Packaging
Beyond the established options of paper and bioplastics, exciting research is underway into innovative materials like mushroom packaging and seaweed-based films. Mushroom packaging, crafted from mycelium (the root structure of mushrooms), is compostable and provides exceptional cushioning. This makes it ideal for protecting delicate food items during transport.
Seaweed extracts can be transformed into films suitable for packaging a variety of food products. These biodegradable films offer a natural barrier against moisture and oxygen, potentially replacing conventional plastic films and further reducing reliance on non-renewable resources. This represents a promising avenue for sustainable packaging innovation.
Navigating Material Selection
Selecting the right sustainable packaging material demands a careful evaluation of numerous factors. Food preservation, environmental impact, cost-effectiveness, and scalability all influence the decision-making process. This can be especially complex for businesses with diverse product lines. For example, packaging dry goods versus fresh produce will likely require different materials for optimal preservation. The unique requirements of each product must be carefully considered.
To assist in this process, the following table summarizes key characteristics of various sustainable food packaging materials:
| Material Type | Environmental Impact | Average Cost | Shelf-Life Extension | Adoption Rate | Best Food Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper/Paperboard | High Recyclability | Low | Moderate | High | Dry goods, frozen foods |
| Bioplastics | Biodegradable, Compostable | Moderate to High | Moderate to High | Increasing | Fresh produce, snacks |
| Mushroom Packaging | Compostable | High | High | Low | Fragile items |
| Seaweed Films | Biodegradable | Moderate | Moderate to High | Low | Snacks, dry goods |
This table offers a general overview. The optimal choice depends on the specific needs of each product. Companies must carefully balance sustainability benefits against practical considerations. Discover more insights about this topic. By understanding each material's unique properties, businesses can choose the most suitable option and contribute to a more sustainable future for the food industry. This careful selection process is essential for maximizing both product quality and environmental responsibility.
Turning Regulations Into Competitive Advantage

Regulations surrounding sustainable food packaging can often feel like obstacles. However, forward-thinking companies are turning these requirements into opportunities to outpace the competition. This proactive strategy not only ensures compliance but also fosters consumer trust and solidifies market position. This section offers practical guidance on navigating the complex landscape of packaging regulations and leveraging them for a competitive edge.
Understanding the Regulatory Landscape
Regulations differ substantially across various markets. The European Union, for example, has more stringent rules on single-use plastics than other regions. This demands a detailed understanding of the specific regulations within each target market.
Companies must be adaptable in their packaging strategies. Staying ahead of proposed changes allows for proactive adjustments, avoiding expensive last-minute overhauls. This foresight positions businesses as leaders in sustainability.
Leveraging Certification and Labeling
Certification standards, such as those from reputable organizations, showcase a commitment to sustainable practices. These certifications offer independent verification of a company’s efforts, building consumer confidence.
For example, a company might pursue certification for using recycled content in their packaging. This third-party validation reinforces trust and demonstrates a genuine commitment that goes beyond simple marketing statements. Material innovations are key to sustainable packaging. For further insights, explore this infographic on the return of green packaging products.
Transparent labeling is another valuable tool. Clearly communicating the sustainable aspects of packaging, such as recyclability or compostability, empowers consumers to make informed decisions.
This transparency strengthens a brand's image as a responsible entity. Using straightforward language like "100% recyclable" or "Made with compostable materials" removes ambiguity and resonates effectively with consumers.
Verification and Traceability
Robust verification processes, including regular audits and supply chain transparency, ensure continued compliance and prevent greenwashing. These processes substantiate a company’s sustainability claims, building credibility with stakeholders and demonstrating accountability.
Today’s consumers are discerning and can readily identify inauthentic claims. Verification processes safeguard against reputational damage and cultivate enduring consumer trust.
Turning Compliance Into Differentiation
Leading food brands are moving beyond simple compliance and utilizing sustainability as a key differentiator. By embracing sustainable mandates early on, companies can build a robust reputation for environmental responsibility.
This proactive approach enhances brand image, attracts environmentally conscious consumers, and ultimately fuels market share growth. It positions them not simply as compliant, but as industry pioneers.
Case Studies: Success Through Sustainability
Many companies have effectively transformed regulatory hurdles into market advantages. For instance, a company that proactively adopted compostable packaging before it became mandatory gained a significant edge.
They cultivated a loyal customer base by being early adopters. This forward-thinking approach enabled them to build brand loyalty and secure market share before competitors could react. These success stories showcase the potential of turning regulatory challenges into narratives of innovation and market leadership. By embracing sustainability, companies generate value for both their business and the environment.
Overcoming Implementation Barriers That Stop Most Brands
Switching to sustainable food packaging offers many benefits, but it's also challenging. Many brands face roadblocks. This section explores these common barriers and offers solutions from companies that have successfully transitioned.
Managing Costs and Budgets
A major hurdle is the perceived higher cost of sustainable materials. Some sustainable options might initially cost more than traditional packaging. However, this perception often misses long-term cost savings. Lighter materials can reduce shipping costs, and minimizing packaging waste can lower disposal fees.
A full cost analysis is essential. This means looking at material costs alongside potential savings. This approach reveals the real economic advantages of sustainable packaging.
Integrating With Existing Production Lines
Introducing new materials into current production lines can be difficult. This might involve equipment changes or adjustments to production methods. However, a step-by-step approach can ease this process.
A company might transition one product line to compostable packaging before scaling up. This allows for adjustments and minimizes overall disruptions.
Maintaining Product Quality and Shelf Life
Preserving product quality and shelf life is critical. Sustainable packaging materials must protect against moisture, oxygen, and other elements. Thorough testing is vital to ensure the packaging effectively protects the product and meets shelf life requirements. This is especially important for perishable foods.
Securing Stakeholder Buy-In
Getting everyone on board – from internal teams to suppliers and retailers – is essential. Clearly explaining the environmental and financial benefits of sustainable packaging is key. This might include showing data on reduced waste or the positive impact on brand image.
Naked Pantry, a company focused on plastic-free products, emphasizes the dangers of microplastics in food to connect with health-conscious consumers. By making a strong case for sustainability, companies can build support and drive change.
Practical Strategies for Successful Implementation
Sustainable packaging implementation takes planning and execution. These strategies can help:
- Phased Implementation: Start small with a pilot project and expand gradually.
- Supplier Collaboration: Working with suppliers offers valuable expertise and assistance.
- Testing and Evaluation: Thorough testing ensures the packaging meets all requirements.
- Clear Communication: Keeping everyone informed encourages support and smoother transitions.
- Measure and Track Progress: Monitoring metrics like waste reduction and cost savings shows the value of sustainable practices. This data helps identify areas for improvement and justifies continued investment.
By using these strategies and addressing challenges proactively, brands can effectively adopt sustainable packaging, gaining environmental and financial advantages. This approach positions them as responsible companies and sets them up for future success.
The Future of Sustainable Food Packaging Is Here

The transition to sustainable food packaging is gaining momentum. What were once innovative concepts are now becoming practical solutions. This exploration of emerging technologies reveals how the industry is evolving, paving the way for a more environmentally friendly future. From enhancing product longevity to revolutionizing recycling processes, these advancements offer significant environmental and economic advantages.
Smart Packaging: Extending Shelf Life and Reducing Waste
Smart packaging integrates technology to monitor and preserve food quality. This innovative approach extends shelf life and minimizes waste by acting as a built-in freshness tracker. Freshness sensors, for example, detect spoilage gases, providing consumers with real-time information about a product's quality. This proactive approach reduces food waste at the consumer level and enhances product safety.
Time-temperature indicators offer a visual record of a product's temperature history. This is particularly important for temperature-sensitive items like fresh produce or dairy, ensuring they have been stored correctly throughout the supply chain. This helps maintain quality and safety, playing a crucial role in reducing waste and preserving product integrity.
Closed-Loop Systems: A Circular Approach to Packaging
Closed-loop systems focus on keeping materials in use for as long as possible, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. Refillable packaging, where consumers return empty containers for cleaning and reuse, is a prime example. Several companies are already embracing this model, demonstrating its viability and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Designing packaging for recyclability is another key aspect of closed-loop systems. Mono-material packaging, made from a single type of plastic, simplifies the recycling process. This reduces contamination and facilitates the creation of new packaging from recycled materials, fostering a true circular economy.
Packaging-as-a-Service: Rethinking Ownership and Responsibility
Packaging-as-a-Service (PaaS) presents a new paradigm in the packaging industry. Instead of owning packaging outright, businesses lease it from a provider who manages cleaning, sanitization, and reuse. This model streamlines logistics and minimizes waste for companies while promoting a sustainable approach to packaging management. PaaS can be particularly advantageous for small to medium-sized businesses lacking the resources to manage their own closed-loop systems.
Advances in Recyclability: Transforming Waste into Resources
Innovations in recycling technologies are unlocking the potential of materials that were previously challenging to recycle. Advanced sorting and processing methods enable the recovery of valuable resources from waste streams. This reduces the strain on landfills and provides a source of recycled materials for new packaging production. These developments are crucial for progressing towards a circular economy and reducing the environmental footprint of packaging.
Early Adopters and Competitive Advantages
Forward-thinking food companies are integrating these technologies to gain a competitive edge. Some brands are using compostable packaging for their products. Others are exploring edible films derived from seaweed or other natural materials. These initiatives not only minimize environmental impact but also resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing brand image and boosting sales. This highlights the positive relationship between sustainability and profitability. The future of sustainable food packaging isn't just about mitigating environmental harm; it's about creating a more resilient and responsible food system.
Your Roadmap to Sustainable Packaging Success
To understand the future benefits of sustainable food packaging, consider how optimizing the input (packaging) can positively affect the output (the consumer's health and wellness). Read more about digestive wellness. Transforming your food packaging to be more sustainable requires a structured approach. This section outlines a practical framework for food businesses to achieve sustainable packaging success, balancing environmental responsibility with business realities.
Assessing Your Current Packaging Portfolio
Begin by thoroughly analyzing your current packaging. This involves understanding the materials used, the volume employed, and their end-of-life management (recycling rates, compostability). Identify areas where sustainable alternatives can be easily implemented and those requiring more significant changes. This assessment creates a baseline for measuring progress.
Setting Meaningful Sustainability Goals
Establish clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) sustainability goals. These might include reducing plastic usage by a certain percentage, increasing the use of recycled content, or achieving specific certifications for sustainable sourcing. For example, aim for a 20% reduction in plastic packaging within two years. Quantifiable goals provide direction and benchmarks.
Prioritizing High-Impact Changes
Focus on areas where changes will yield the greatest environmental benefit. Perhaps switching to compostable packaging for specific product lines will have a larger impact than minor changes across all packaging. Prioritizing ensures that efforts are concentrated where they matter most.
Collaboration and Communication
Successful implementation requires cross-functional collaboration. Engage teams from procurement, production, marketing, and sales. Open communication ensures everyone understands the sustainability goals and their role in achieving them. This fosters a shared commitment throughout the organization.
Managing the Transition: A Phased Approach
Implement changes incrementally, perhaps focusing on one product line initially, to minimize disruption. This phased approach allows for adjustments and learning before full-scale implementation, minimizing risk and maximizing the chances of long-term success.
Measuring and Demonstrating Value
Track your progress toward your sustainability goals. Measure reductions in waste, cost savings from material optimization, and any positive impact on brand perception. This data demonstrates the tangible business value of your sustainability initiatives, providing evidence of your success and strengthening the case for continued investment.
Successfully implementing sustainable packaging improves your brand image, reduces environmental impact, and can create long-term cost savings. Start making these changes today and join the movement toward a more sustainable future.
Ready to embark on your plastic-free journey? Discover how Naked Pantry delivers sustainable pantry staples right to your door. Visit them today!
Article created using Outrank
